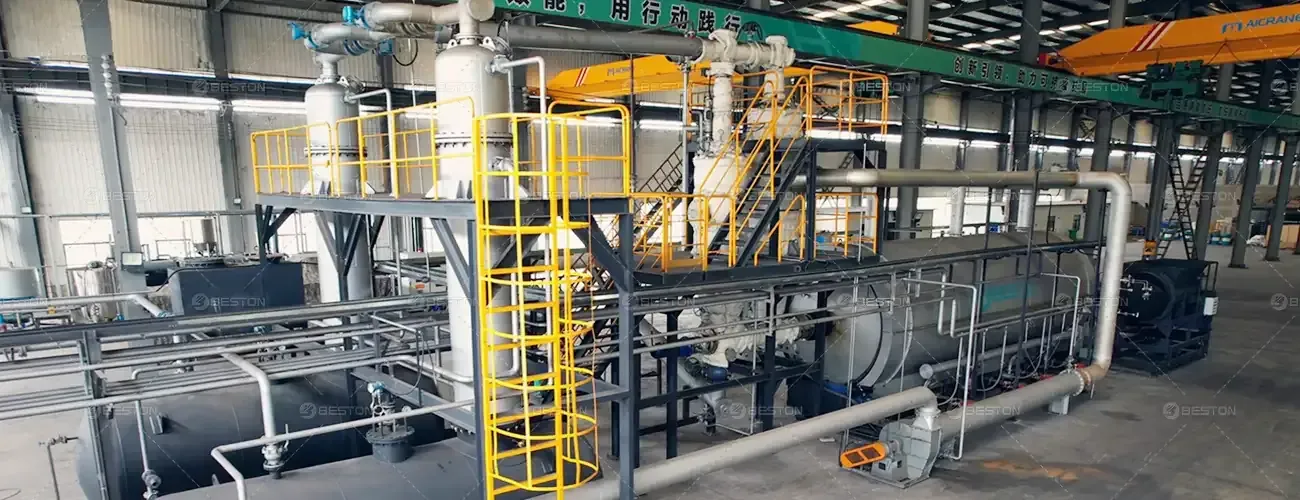
Waste Rubber Recycling: The Efficiency Boost of Continuous Pyrolysis Technology
In the realm of waste management, the integration of advanced technologies has become paramount, and continuous pyrolysis technology stands as a transformative force in improving the efficiency of waste rubber recycling. This cutting-edge approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also maximizes resource recovery from discarded rubber materials. Let's delve into the intricacies of continuous pyrolysis and how it reshapes the landscape of waste rubber recycling.
Unveiling Continuous Pyrolysis Technology
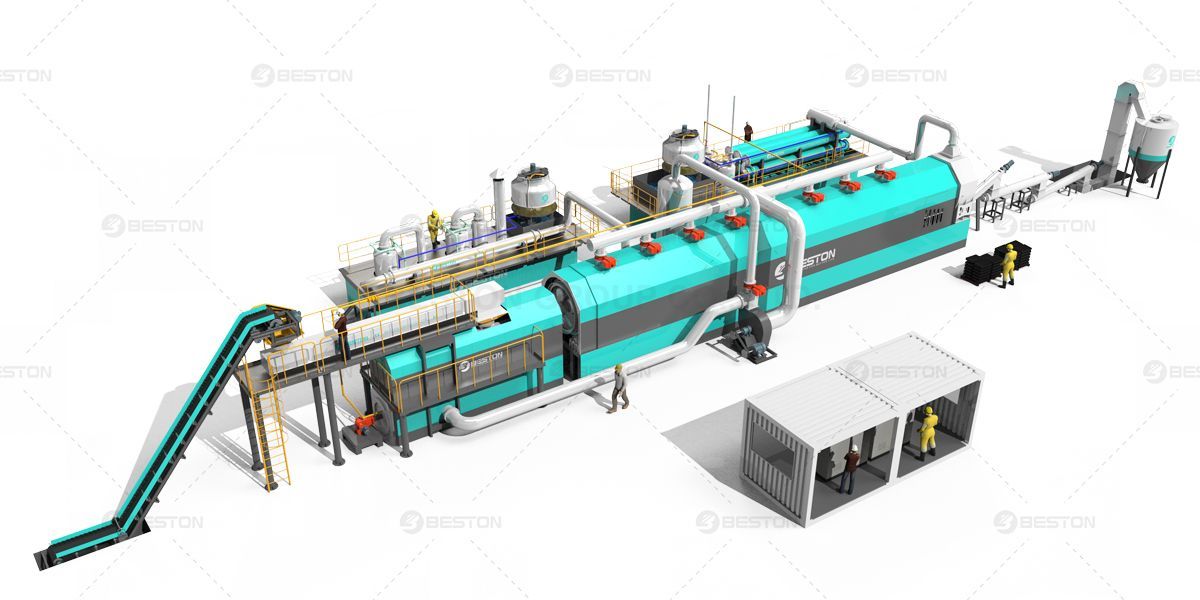
At the core of this revolutionary process lies continuous pyrolysis, a thermal decomposition method operating in a controlled environment. Unlike traditional batch pyrolysis systems, the fully continuous pyrolysis plant is designed for uninterrupted operation, enhancing both the scale and efficiency of waste rubber recycling.
Continuous Operation Dynamics
The term "fully continuous" encapsulates the essence of seamless operation. The continuous pyrolysis plant functions around the clock, without the need for intermittent halts in the recycling process. This continuous operation ensures a steady flow of waste rubber through the pyrolysis reactor, optimizing both time and resource utilization.
Maximizing Efficiency in Waste Rubber Recycling
Enhanced Feeding Requirements
The efficiency gains of continuous pyrolysis technology are notably reflected in the optimized feeding requirements. The system allows for a continuous and automated feeding process, ensuring a consistent supply of waste rubber into the pyrolysis reactor. This automation minimizes downtime associated with manual loading, contributing to increased overall efficiency.
Rubber Powder Utilization
A distinguishing feature of waste rubber recycling through continuous pyrolysis is the utilization of rubber powder. The plant can efficiently process rubber powder, a finely ground form of waste rubber. This capability expands the scope of acceptable feedstock, allowing for the recycling of rubber materials in various states and forms.
The Pyrolysis Process Unveiled
Controlled Thermal Decomposition
Within the confines of the pyrolysis reactor, waste rubber undergoes controlled thermal decomposition. The absence of oxygen in this environment prevents combustion, leading to the breakdown of complex rubber polymers into valuable byproducts. These byproducts include pyrolysis oil, syngas, and carbon black.
Syngas Generation: A Clean Energy Source
One of the advantageous outcomes of the pyrolysis process is the generation of syngas. This gaseous mixture, rich in hydrogen and carbon monoxide, serves as a clean energy source. The fully continuous pyrolysis plant facilitates the continuous extraction and utilization of syngas, contributing to sustainable energy practices.
Pyrolysis Oil: A Versatile Resource
The liquid yield from pyrolysis, known as pyrolysis oil, emerges as a versatile resource with myriad applications. From industrial processes to fuel production, the continuous generation of pyrolysis oil ensures a consistent supply of this valuable liquid, adding to the overall efficiency of the waste rubber recycling process.
Environmental Stewardship
Mitigating Environmental Impact
Continuous pyrolysis technology aligns with environmental stewardship goals by mitigating the environmental impact of waste rubber disposal. The controlled thermal decomposition reduces emissions compared to traditional incineration methods, offering a more sustainable approach to rubber waste management.
Closed-Loop Systems
In a bid to minimize wastage and enhance sustainability, many fully continuous rubber pyrolysis plants incorporate closed-loop systems. These systems recycle excess heat generated during the pyrolysis process, optimizing energy utilization within the plant and minimizing the environmental footprint.
Economic Viability
Continuous Operational Benefits
From an economic standpoint, the continuous nature of waste rubber recycling with pyrolysis technology translates into continuous operational benefits. The seamless operation minimizes downtime, maximizing the return on investment for businesses venturing into continuous pyrolysis.
Scalability: Tailoring Solutions to Demand
The modular design of many fully continuous pyrolysis plants adds a scalability dimension. Businesses can scale their operations to match the evolving demands of rubber waste processing, making continuous pyrolysis a versatile solution for various scales of waste management.
Future Outlook
Technological Advancements
Continuous pyrolysis technology is poised for ongoing advancements. Research and development efforts aim to enhance the efficiency, automation, and environmental performance of fully continuous pyrolysis plants. Continuous innovation holds the promise of further optimizing waste rubber recycling processes.
Global Adoption
The benefits of continuous pyrolysis in waste rubber recycling are gradually gaining global recognition. As environmental regulations tighten and sustainability practices become integral to waste management strategies, the adoption of continuous pyrolysis technology is expected to proliferate across industries and regions.
In Conclusion: A Sustainable Evolution
Continuous pyrolysis technology, especially in the context of waste rubber recycling, represents a sustainable evolution in waste management practices. The efficiency gains, environmental benefits, and economic viability position this technology as a pivotal player in the journey towards a greener and more resource-efficient future.



