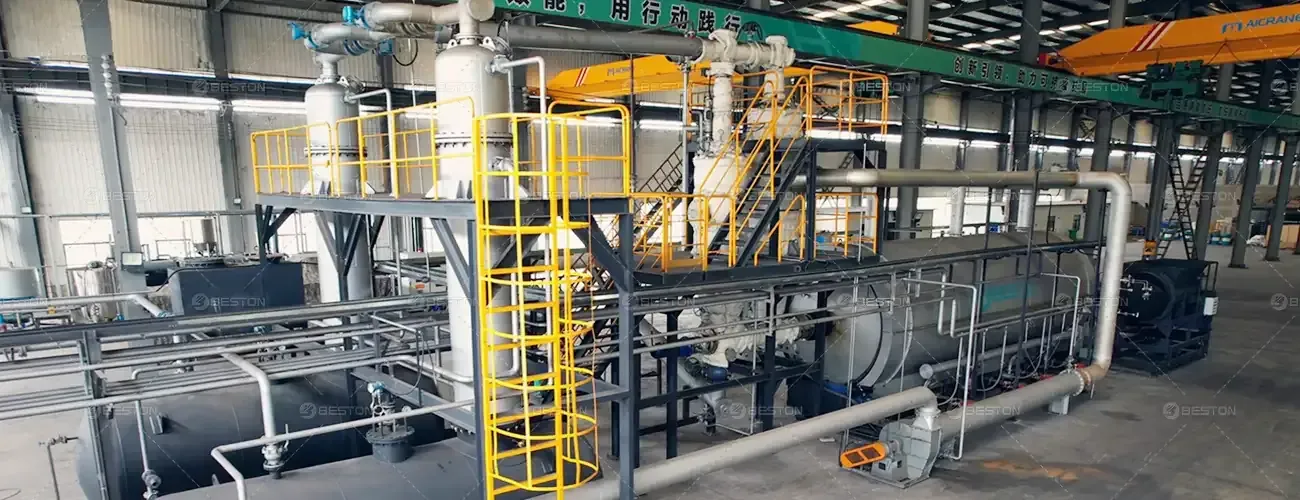
What exactly is a Continuous Pyrolysis Plant and How Can it Work
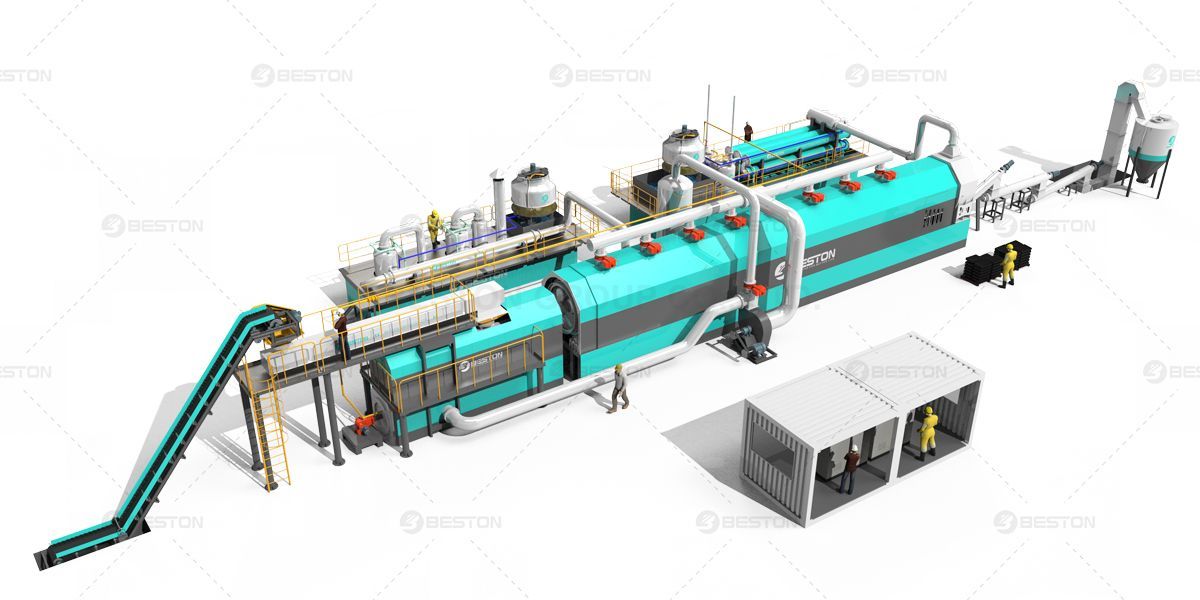
A continuous pyrolysis plant is a kind of waste management facility that is able to convert organic waste matter into combustible gas along with other useful products. This method, known as pyrolysis, occurs when the organic matter is heated in the absence of oxygen. The resulting products might include such things as charcoal, bio-oil, and synthesis gas, which bring fuel for power generation or some other industrial processes. Continuous pyrolysis plants are usually large-scale facilities that can handle high volumes of waste. Therefore, they are generally utilized by municipalities or some other organizations that generate a lot of organic waste.
Working mechanism
This particular plant essentially is made up of four main parts: a feeder, reactor, condenser, and gasifier. The feeder can be used introducing the material being pyrolyzed in the reactor. The reactor is the place where the specific technique of pyrolysis happens. It can be heated to a quite high temperature (usually between 700-900 degrees Celsius) in order to break up the hydrocarbon chains. The vapor and gas manufactured in the reactor are then passed throughout the condenser, where they may be cooled and condensed back into liquid form. Finally, the gasifier is commonly used to get rid of any solid impurities that could remain after condensation.
The full process takes place beneath a vacuum in order to prevent oxygen from getting into experience of the hydrocarbons and causing these people to burn. When operated correctly, a continuous pyrolysis plant can acquire a quite high degree of hydrocarbon conversion. This will make it a stylish choice for waste disposal and recycling, and for producing fuel and other valuable chemicals from organic materials.
Features of employing a continuous pyrolysis plant
A continuous pyrolysis plant offers numerous advantages over other waste disposal methods, such as incineration and landfill. Pyrolysis is really a thermal decomposition method that stops working organic matter into combustible gases and char. The gases may be used to generate electricity, whilst the char can be used as a soil amendment. Furthermore, the continuous pyrolysis process is tremendously efficient, with minimal to no waste material left over. As opposed, incineration leaves behind hazardous ash that really must be disposed of within a landfill, while landfill brings about the generation of methane gas, and that is a major reason for climate change. Continuous pyrolysis is therefore a much more environmentally-friendly choice for waste disposal.
Choosing the best continuous pyrolysis plant
When you are looking for a continuous pyrolysis plant, there are a few things you should bear in mind to ensure you choose the best one for your requirements. First, consider the capacity in the plant. You will want to choose a plant that could handle the quantity of waste you generate on a daily basis. Second, consider the type of waste you will certainly be processing. Some plants are equipped for specific kinds of waste, including plastics or tires. Be sure the plant you end up picking can handle the kind of waste you may be feeding it. Finally, consider the expense of the plant. It is advisable to choose a plant which is affordable and definately will fit within your budget.
The continuous pyrolysis plant is surely an efficient way to break up these materials and turn them into valuable products. If you are searching for starting your very own pyrolysis plant, ensure you compare different plants before purchasing one.



