Biochar Application in Forestry

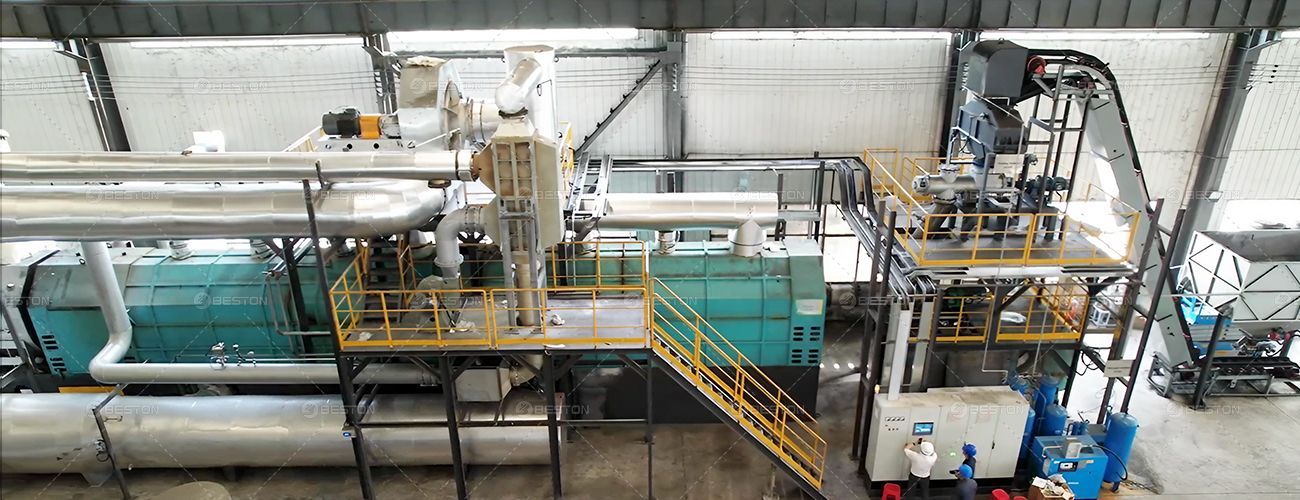
Forestry management practices are evolving with the integration of innovative technologies and sustainable solutions. Among these advancements, biochar pyrolysis equipment has garnered attention for its potential applications in enhancing soil health, promoting reforestation efforts, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Understanding Biochar:
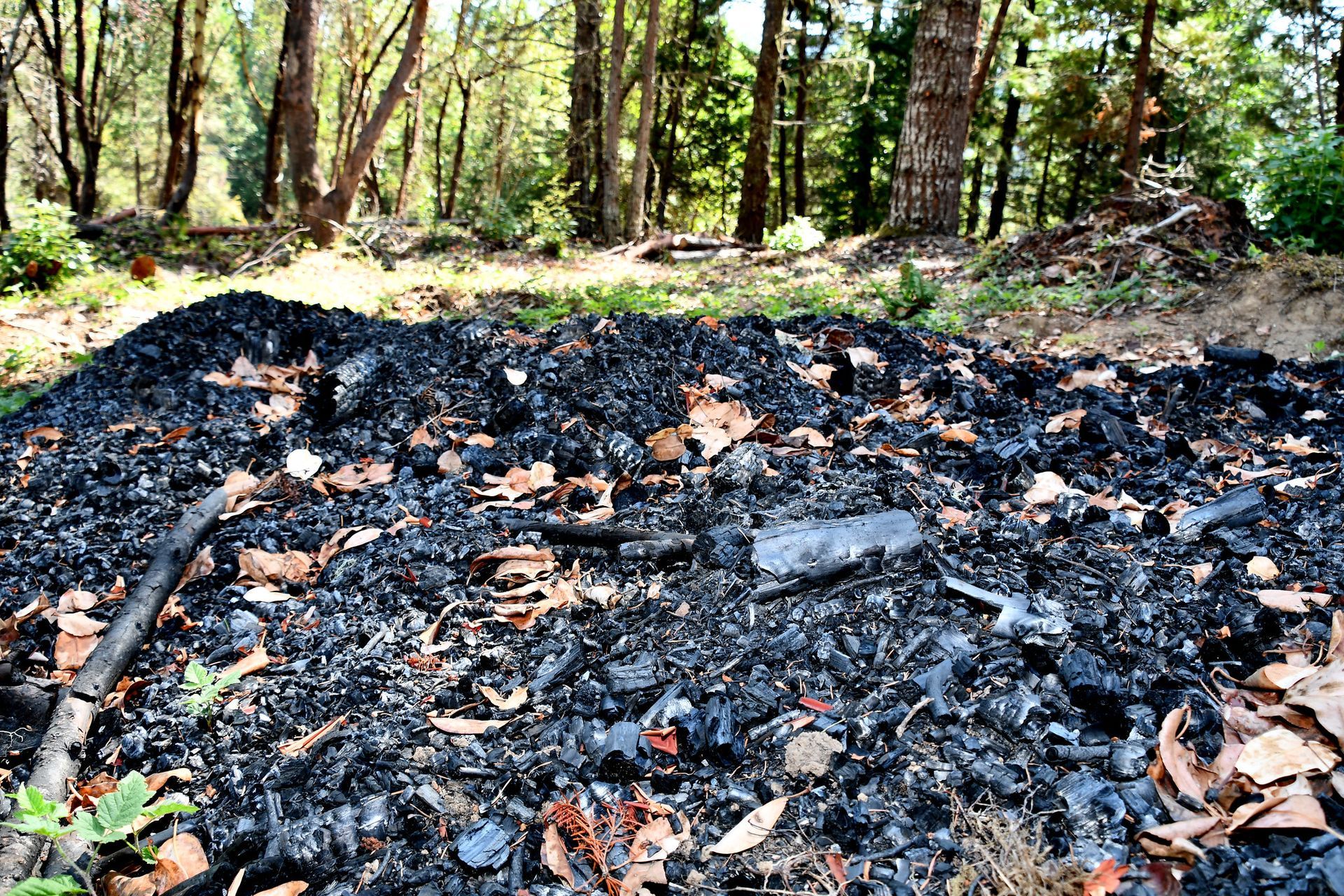
Biochar, a carbon-rich material produced through the pyrolysis of biomass, holds immense promise in forestry applications. Pyrolysis, a thermochemical process, involves heating organic matter in the absence of oxygen to produce a stable form of carbon known as biochar. This process not only sequesters carbon from biomass but also transforms it into a valuable soil amendment with unique properties.
Soil Amendment and Nutrient Retention:
One of the primary applications of biochar in forestry is its use as a soil amendment. Incorporating biochar into forest soils improves soil structure, enhances water retention capacity, and promotes nutrient cycling. The porous nature of biochar provides habitat for beneficial microorganisms and enhances microbial activity in the soil, leading to increased nutrient availability for tree growth and establishment.
Erosion Control and Slope Stabilization:
In areas prone to erosion and soil degradation, biochar can play a vital role in erosion control and slope stabilization. By amending soils with biochar, forestry practitioners can improve soil stability, reduce runoff, and minimize soil erosion on steep slopes. The enhanced water infiltration and retention properties of biochar help mitigate the impacts of heavy rainfall events and prevent soil loss, thereby promoting ecosystem resilience and long-term forest health.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation:
The incorporation of biochar into forest soils contributes to long-term carbon sequestration, thereby mitigating the impacts of climate change. As biochar is recalcitrant and resistant to decomposition, the carbon captured during pyrolysis remains stored in the soil for hundreds to thousands of years. This sequestered carbon helps offset greenhouse gas emissions and reduces the carbon footprint of forestry operations, making biochar a valuable tool in climate change mitigation strategies.
Restoration of Degraded Lands:
Biochar application holds promise for restoring degraded forest lands and promoting ecosystem recovery. In areas affected by deforestation, mining activities, or wildfires, biochar can improve soil fertility, accelerate vegetation regrowth, and facilitate ecosystem recovery. The incorporation of biochar into degraded soils enhances their resilience to environmental stressors and fosters the establishment of diverse plant communities, ultimately leading to the restoration of healthy and functioning forest ecosystems.
Enhancement of Tree Health and Resilience:
By improving soil conditions and nutrient availability, biochar application can enhance the health and resilience of forest trees. The presence of biochar in the soil promotes root development, increases nutrient uptake efficiency, and reduces susceptibility to soil-borne pathogens and diseases. Healthy and resilient trees are better equipped to withstand environmental stressors such as drought, pests, and diseases, thereby contributing to overall forest vitality and sustainability.
Utilization of Forest Biomass Residues:
The production of biochar from forest biomass residues offers a sustainable solution for utilizing waste materials and reducing environmental impacts. By converting logging residues, forest thinnings, and woody biomass into biochar through pyrolysis, forestry operations can minimize waste generation and mitigate the release of greenhouse gases from biomass decomposition. This closed-loop approach maximizes the utilization of forest resources while promoting soil health and ecosystem sustainability.
Research and Innovation:
Ongoing research and innovation in biochar production technologies and forestry applications continue to expand the potential benefits of biochar in forestry management. Advances in biochar pyrolysis equipment improve production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and enhance biochar quality, making it more accessible and cost-effective for forestry practitioners. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations between scientists, foresters, and policymakers facilitate knowledge exchange and the development of best practices for biochar utilization in forestry.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, biochar holds significant promise as a sustainable solution for enhancing soil health, promoting reforestation efforts, and mitigating the impacts of climate change in forestry. Through the application of biochar produced using advanced biochar pyrolysis equipment, forestry practitioners can improve soil fertility, reduce erosion, sequester carbon, and enhance the resilience of forest ecosystems. As research and innovation in biochar continue to advance, its role in forestry management is expected to grow, contributing to the sustainable stewardship of forest resources for future generations.