Differences Between Plastic Pyrolysis and Tyre Pyrolysis
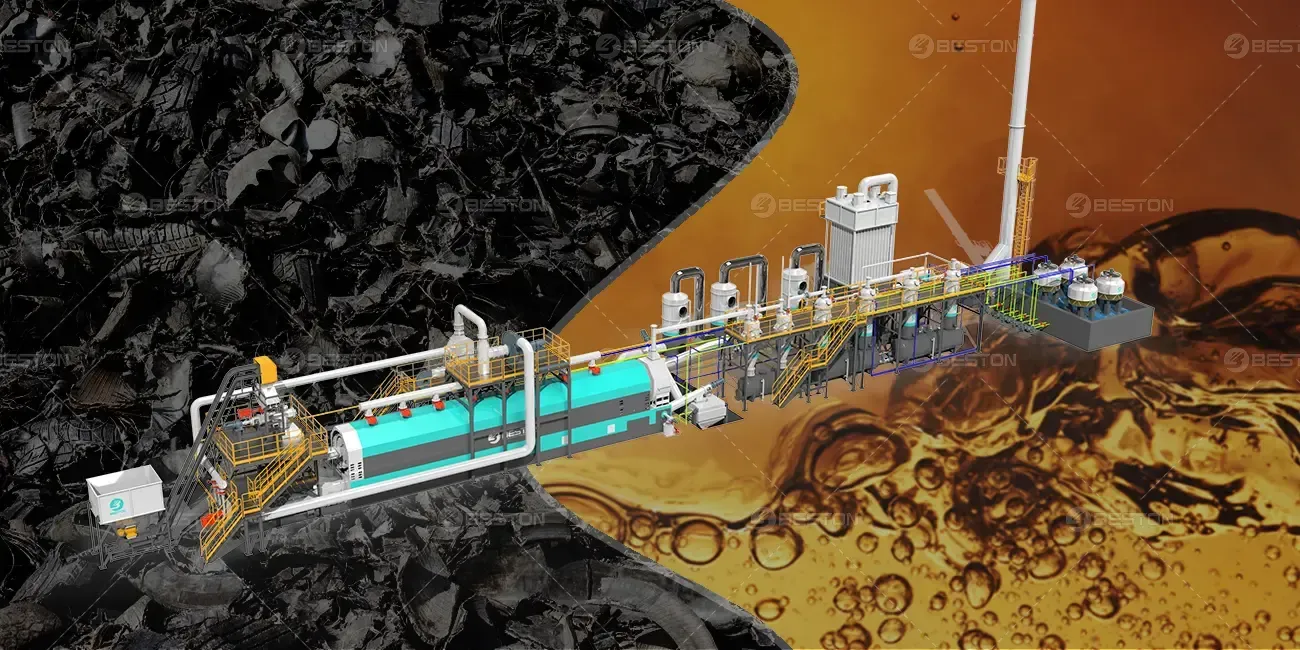
The processes of plastic pyrolysis and tyre pyrolysis are two methods used for converting waste into valuable products through thermal decomposition. While both methods involve similar principles, they differ significantly in their feedstocks, processes, and outputs. This analysis explores these differences in detail, focusing on the technologies involved, the types of machines used, and the products generated.
Feedstock Characteristics
Plastic Feedstock
Plastics, derived from petrochemical sources, vary widely in composition and properties. Common plastics used in pyrolysis include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS). Each type of plastic has distinct characteristics, such as molecular weight and chemical structure, which influence the pyrolysis process.
Plastic to oil machine processes are designed to handle these diverse plastic types, often requiring pre-processing to ensure uniformity. Contaminants and additives in plastics can affect the efficiency and quality of the output, necessitating thorough sorting and cleaning.
Tyre Feedstock
Tyres, primarily composed of natural and synthetic rubber, along with steel and textile fibers, present a more complex feedstock. The composition of tyres can vary based on their type and manufacturer, but they generally consist of a mixture of rubber polymers, carbon black, and other chemicals.
The tyre to oil machine must address the challenges posed by the mixed material composition. Tyres often require additional preprocessing to remove non-rubber components and reduce particle size, which can impact the efficiency of the pyrolysis process.
Pyrolysis Process
Plastic Pyrolysis
Plastic pyrolysis involves the thermal decomposition of plastic materials in the absence of oxygen. The process typically occurs at temperatures ranging from 300°C to 900°C, depending on the type of plastic and the desired output. The plastic to oil machine for sale facilitates this process by providing controlled heating and an inert atmosphere to prevent combustion.
The pyrolysis of plastics results in a mixture of liquid hydrocarbons (oil), gaseous products, and solid residues (char). The composition of the oil can vary based on the plastic type and pyrolysis conditions. The oil produced is often used as a feedstock for further refining or as a substitute for conventional fuels.
Tyre Pyrolysis
Tyre pyrolysis, while similar in principle to plastic pyrolysis, requires higher temperatures, typically between 400°C and 800°C. The tyre to oil machine is designed to accommodate the unique properties of tyre feedstock, such as its high carbon content and the presence of metal and fiber components.
The pyrolysis of tyres yields three primary products: tyre oil, carbon black, and steel wire. The oil produced from tyres can be used as an alternative fuel or refined further for various applications. The carbon black, a byproduct of the process, has potential uses in manufacturing and industrial applications.
Machine Technology
Plastic to Oil Machine
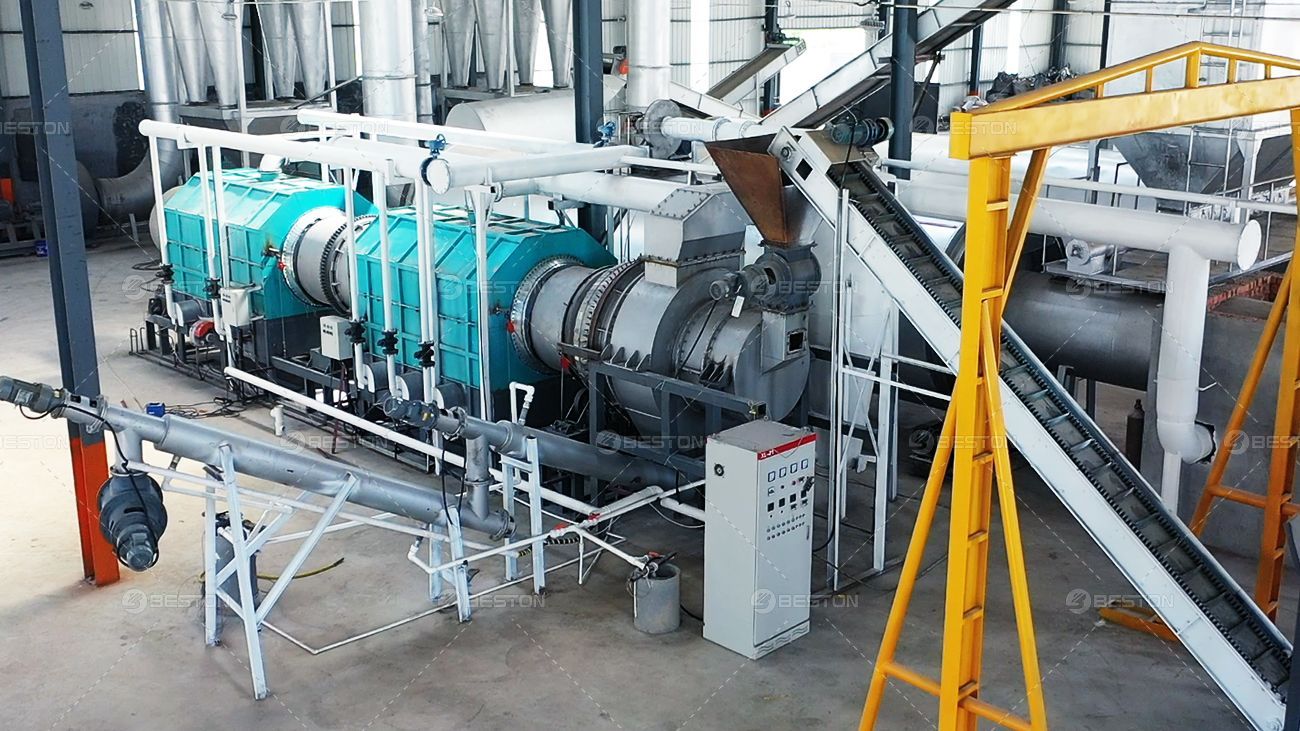
The plastic to oil machine is specifically engineered to handle a wide range of plastic materials. It typically features advanced heating systems, such as rotary kilns or batch reactors, that ensure precise temperature control and efficient thermal decomposition. Some machines include features for continuous processing, allowing for a steady flow of feedstock and product output.
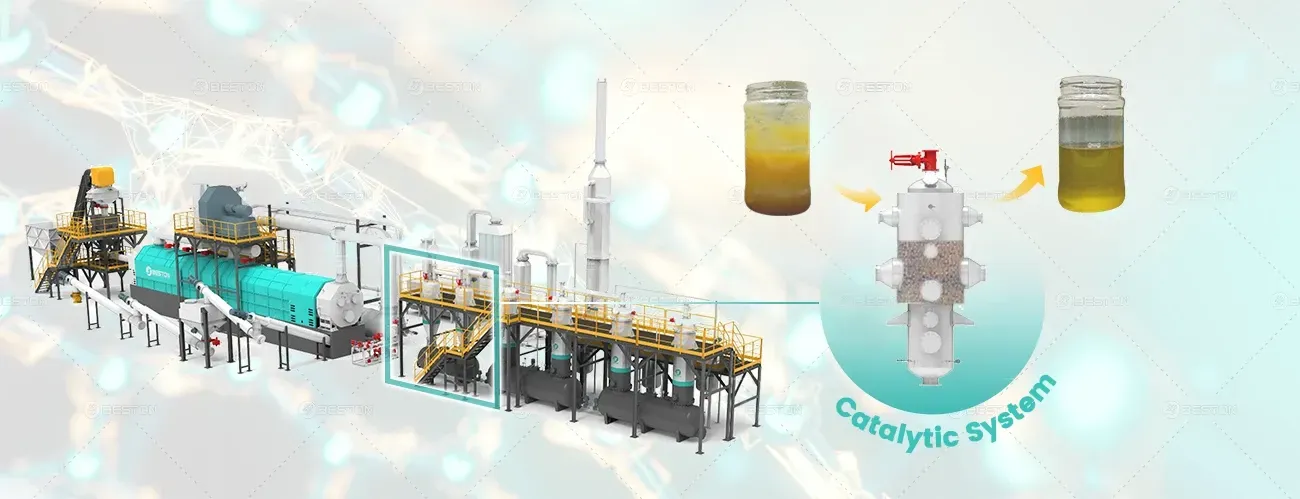
Modern plastic to oil machines may also incorporate catalytic processes to enhance the quality of the oil produced. Catalysts can help break down complex polymers into more desirable hydrocarbons, improving the efficiency of the conversion process.
Tyre to Oil Machine
The tyre to oil machine, designed to process whole tyres, includes robust and durable components to handle the harsh conditions of tyre pyrolysis. This machine often features pre-processing units for shredding and separating the steel and textile fibers from the rubber.
Advanced tyre to oil machine utilizes rotary reactors or screw-type reactors to facilitate the pyrolysis process. These machines are built to manage the high carbon content of the feedstock and to ensure efficient separation of the various byproducts. Some systems also include additional steps for cleaning and refining the produced oil.
Product Output
Plastic Pyrolysis Products
The primary products of plastic pyrolysis are liquid hydrocarbons (plastic oil), gas, and char. The composition of the plastic oil depends on the type of plastic and the pyrolysis conditions. It can be used as a fuel or further refined into various chemicals.
The gaseous products produced during plastic pyrolysis often include methane, ethylene, and propane. These gases can be captured and utilized as energy sources for the pyrolysis process or other applications. The solid residue, primarily carbon, has limited uses but can be processed further if necessary.
Tyre Pyrolysis Products
Tyre pyrolysis generates three main products: tyre oil, carbon black, and steel wire. Tyre oil, similar to the oil produced from plastics, can be used as an alternative fuel or further refined for different applications.
Carbon black, a significant byproduct of tyre pyrolysis, has applications in the rubber industry, pigments, and as a reinforcing agent in various materials. The steel wire extracted from tyres can be recycled or used in various industrial processes.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Environmental Impact
Both plastic and tyre pyrolysis offer environmental benefits by converting waste materials into valuable products, thereby reducing landfill use and minimizing environmental pollution. However, the pyrolysis process must be managed carefully to avoid emissions of harmful compounds and ensure the effective handling of byproducts.
Plastic pyrolysis generally has a lower environmental impact compared to tyre pyrolysis due to the absence of metal components and fewer complex chemicals. Tyre pyrolysis, however, requires stringent measures to manage the emissions of sulfur compounds and other potentially harmful substances.
Economic Viability
The economic viability of both plastic and tyre pyrolysis projects depends on factors such as feedstock availability, machine efficiency, and market demand for the products. Plastic to oil machines often have lower operational costs due to the simpler feedstock preparation and processing requirements.
Tyre to oil machines, while more complex and costly, can potentially offer higher returns due to the multiple byproducts generated. The value of carbon black and steel wire can contribute significantly to the overall profitability of tyre pyrolysis projects.
Conclusion
Plastic pyrolysis and tyre pyrolysis are distinct processes with unique characteristics and challenges. Plastic to oil machines and tyre to oil machines are designed to handle specific feedstocks and produce valuable products through thermal decomposition. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing the pyrolysis processes and maximizing the economic and environmental benefits of waste-to-energy technologies.



