Comparison of Environmental Impacts of Pyrolysis and Incineration
Managing waste effectively is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of modern times. Pyrolysis and incineration are two prominent technologies used to treat waste, particularly plastics and other non-biodegradable materials. While both methods aim to reduce landfill dependence, their environmental impacts differ significantly. This article explores the comparative effects of pyrolysis and incineration on the environment, focusing on emissions, resource recovery, and sustainability.
Overview of Pyrolysis
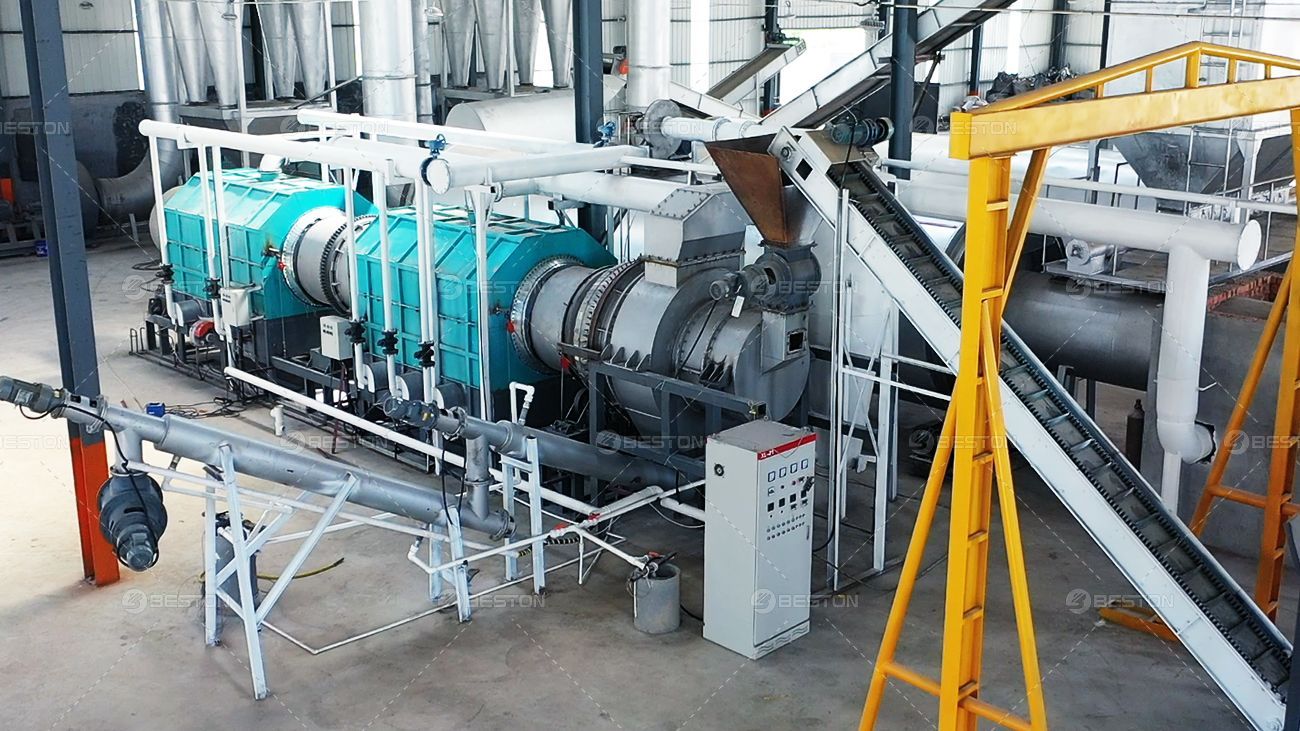
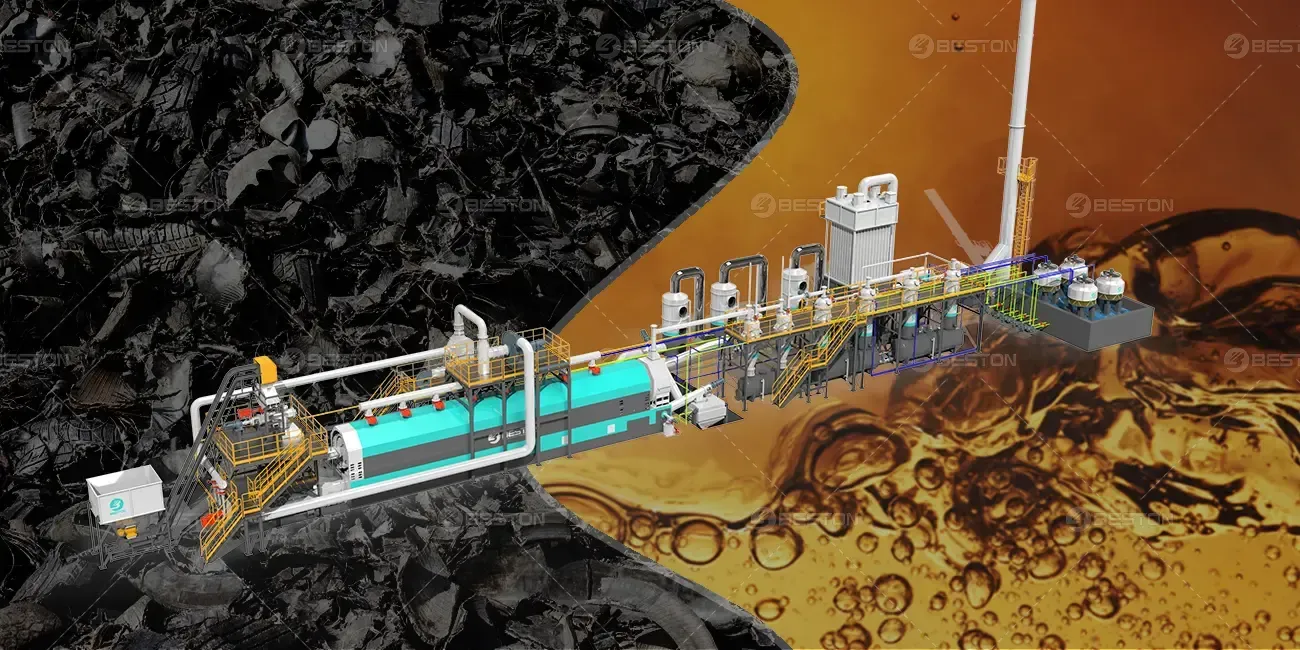
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process conducted in an oxygen-deprived environment. A pyrolysis plant is designed to process waste materials into valuable outputs such as pyrolysis oil, syngas, and char. The process operates at high temperatures, typically ranging from 300°C to 700°C, and avoids combustion, which minimizes direct pollutant release.
Key environmental benefits of pyrolysis include:
- Resource recovery: Produces reusable energy and materials, reducing reliance on virgin resources.
- Lower emissions: Generates fewer toxic byproducts compared to incineration.
Overview of Incineration
Incineration involves burning waste materials at temperatures exceeding 850°C in the presence of oxygen. This process reduces waste volume significantly, but its environmental footprint is considerable. The combustion process releases a range of pollutants, including carbon dioxide, particulate matter, and toxic gases.
Despite its drawbacks, incineration is widely used for its ability to handle mixed and hazardous waste streams.
Emission Comparisons
Pyrolysis
A fully continuous pyrolysis plant generates substantially fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants than incineration. The absence of oxygen prevents the formation of harmful compounds such as dioxins and furans, which are commonly associated with combustion. Additionally, the byproducts of pyrolysis, such as syngas, can be captured and reused as fuel, further reducing emissions.
Incineration
Incineration is a major source of air pollution, releasing large quantities of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and trace metals. While modern incineration plants employ advanced filtration systems, they cannot completely eliminate harmful emissions. Furthermore, the ash generated during incineration may contain heavy metals and other hazardous substances, requiring careful disposal.
Resource Recovery
Pyrolysis
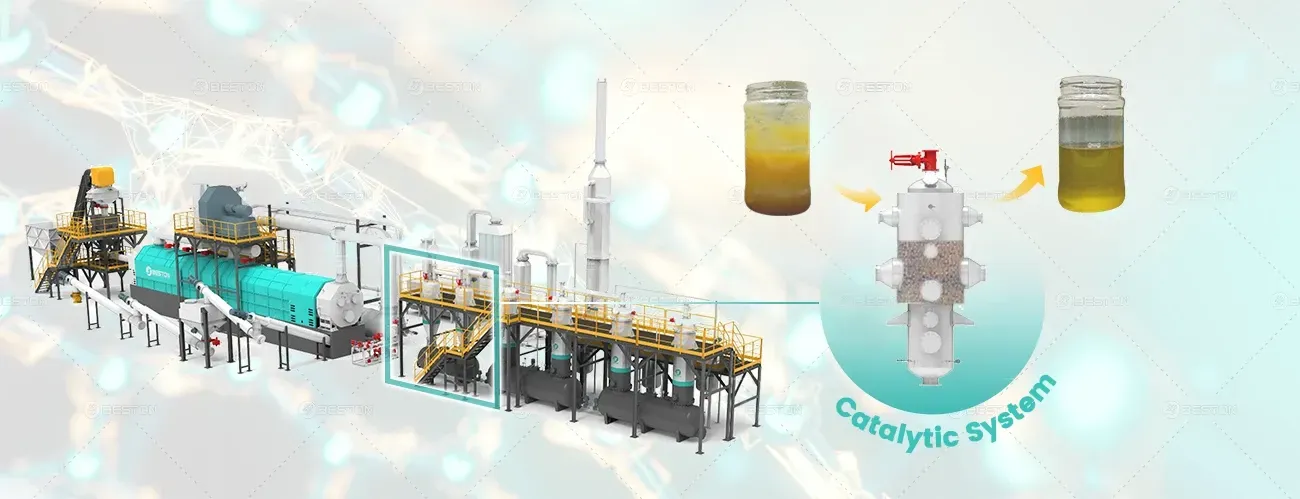
Pyrolysis offers superior resource recovery capabilities. The process transforms waste into usable products like oil, gas, and carbon black. These outputs can replace fossil fuels and other non-renewable materials in various industrial applications, promoting a circular economy.
The flexibility of a pyrolysis plant also allows for the processing of specific waste streams, such as plastics or biomass, to maximize resource recovery.
Incineration
Incineration primarily focuses on waste volume reduction rather than resource recovery. The energy generated during combustion can be harnessed for electricity or heating, but this efficiency is often offset by the energy required to maintain high combustion temperatures. Moreover, incineration leaves behind ash, which typically lacks further utility.
Carbon Footprint
Pyrolysis
The carbon footprint of pyrolysis is significantly lower than that of incineration. By capturing and reusing pyrolysis byproducts, the process ensures minimal net carbon emissions. Additionally, pyrolysis can contribute to carbon offset efforts by reducing the need for fossil fuel extraction and use.
Incineration
Incineration’s high-temperature combustion releases substantial quantities of carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming. Although energy recovery systems can partially mitigate this impact, the overall carbon footprint remains high, particularly when factoring in transportation and handling of waste.
Sustainability Perspective
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis aligns well with sustainability goals by converting waste into valuable secondary resources. The technology supports a circular economy model, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling. Its scalability and adaptability to various waste types make it a long-term solution for sustainable waste management.
Incineration
Incineration is often criticized for its linear approach to waste management. By focusing on waste destruction rather than resource recovery, it perpetuates unsustainable consumption patterns. Furthermore, the environmental risks associated with incineration undermine its suitability as a sustainable waste treatment option.
Conclusion
The environmental impacts of pyrolysis and incineration highlight the superiority of pyrolysis as a cleaner, more sustainable waste management solution. While incineration offers immediate volume reduction, its significant emissions and limited resource recovery capabilities render it less favorable. A pyrolysis plant, on the other hand, not only minimizes pollutants but also contributes to resource conservation, making it a pivotal technology in the transition toward sustainable waste management practices.



